You need to name each of the objects (Table, form, query, report) you create and use in Access.
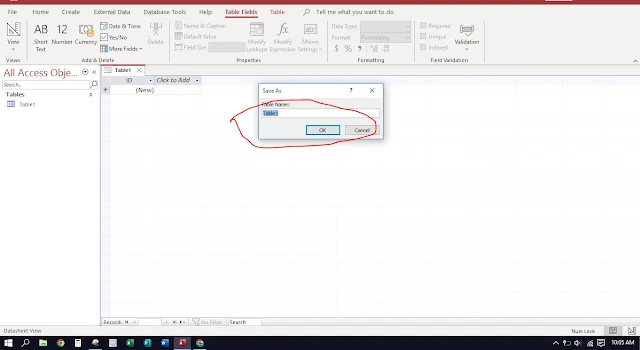
When you first create an object, Access assigns a generic name, such as Table1, Form1, Query 1, Report 1.
The first time you save an object, the Save As dialog box prompts you to enter a different name.
Database designers strongly recommend that you use a meaningful name that describes the contents of the object.
For example, in the DavidoComputerClass database, the tables are named Classes, Departments, and Instructors. This makes it easy to understand the object’s purpose.
Each object typically contains several fields.
Form and report objects may also have other components such as buttons or labels. These components are called controls.
Access naming rules;
Names can have a maximum of 64 characters. The characters can be letters, numbers, and spaces.
You can also use special characters except a period (.), exclamation point (!), square brackets ([ ]), and an accent grave (`).
The name can’t begin with a space.
Note: Although spaces are allowed within a name, most database designers avoid using them due to possible naming conflicts with other applications.
Instead, when creating a compound word name, it is a good idea to start each word with a capital letter (for example, Class1, IntroductionClass).
Sometimes database designers will also include a prefix in the object name such as, tblAccounts or frmSales. The most common prefixes are tbl, used for a table; frm, used for a form; rpt, used for a report; and qry, used for a query.